Getting Started with SEI CMMI
Chapters
SEI CMMI-Maturity Levels
CMM (Capability Maturity Model) is a process maturity for software development. This model describes a five-level evolutionary way of well-organized and systematically mature processes.
Five Maturity Levels of Software Processes in CMMI:
- Initial
- Managed
- Defined
- Quantitatively Managed
- Optimizing
CMMI Staged Representation Maturity Levels:
The maturity levels in a CMMI staged representation as shown below:
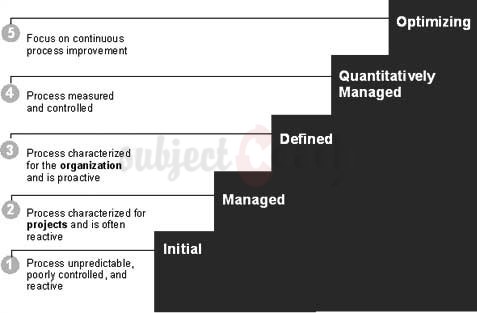
Maturity levels have predefined set of process areas.The achievement of the specific and generic goals in maturity level are measured for each pre-defines set of process.
The CMM model defines five levels of organizational maturity:
Maturity Level 1 Initial:
At the initial level, processes are de-organized and chaotic. individual efforts plays important role in success.
Maturity Level 2 Managed:
There are quantitative indices for both software and process as a whole established in the organization. The decrease of digression in different project indices results in better project management. Here management can effectively control the software development effort using precise measurements.
Maturity Level 3 Defined:
In this level software development and maintenance process are introduced and documented. A transition to more effective technologies occurs with the introduction of standards. There is a special quality management team for building and managing standards.
Maturity Level 4 Quantitatively Managed:
Involving precise measurements, management can effectively control the software development effort. In particular, management can find ways to adopt and adjust to particular process without measurable losses of deviations or quality. At this level organization group a quantitative quality goal for both software maintenance and process.
A difference between maturity level 3 and maturity level 4 is the predictability of process performance. In maturity level 4, the performance of processes is controlled using statistical and quantitative techniques and predictable by quantitatively. In maturity level 3, processes are only qualitatively predictable.
Maturity Level 5 Optimizing:
In the optimizing level, processes are constantly improved through monitoring from current processes feedback and introducing best innovative processes to achieve the organization's particular needs.
Improvements of Process address common causes of process, variation in organization are evaluated and deployed.
Maturity Levels should not be skipped:
One way in which companies are supposed to use the model is first to identify their maturity level and then form a plan to get to the next level. Skipping levels is not allowed.
Without the discipline provided by lower level Higher level processes have less chance of success.
Maturity Levels and Process Areas:
The table below provides more detail on each of the process areas for each of the CMMI maturity levels.
|
Level |
Focus |
Category |
Key Process Area |
Result |
|
5 Optimizing |
Continuous Process Improvement |
Process Management and Support |
Causal Analysis and Resolution (CAR) Organizational Performance Management (OPM) |
Highest Quality / Lowest Risk |
|
4 Quantitatively Managed |
Quantitatively Managed |
Project and Work Management Process Management |
Organizational Process Performance Quantitative Project Management |
Higher Quality / Lower Risk |
|
3 Defined |
Process Standardization |
Service Establishment and Delivery Support Project and Work Management Process Management Engineering Acquisition Engineering |
Decision Analysis and Resolution (DAR) Requirements Development Technical Solution Product Integration Verification Validation Organizational Process Focus Organizational Process Definition Organizational Training Integrated Project Mgmt (with IPPD extras) Risk Management Decision Analysis and Resolution Integrated Teaming (IPPD only)Org. Environment for Integration (IPPD only) Integrated Supplier Management (SS only) |
Medium Quality / Medium Risk |
|
2 Managed |
Basic Project Management |
Project and Work Management Service Establishment and Delivery Support |
Configuration Management (CM) Requirements Management Project Planning Project Monitoring and Control Supplier Agreement Management Measurement and Analysis Process and Product Quality Assurance |
Low Quality / High Risk |
|
1 Initial |
Process is informal and Adhoc |
|
|
Lowest Quality / Highest Risk |
Description
This tutorial is an Introduction to SEI CMMI, This tutorial is sub divided into 9 parts listed below
CONTENTS
Part 1 Introduction
Part 2 Models-Disciplines
Part 3 Representations
Part 4 Maturity Levels
Part 5 Capability Levels
Part 6 Key Process Areas
Part 7 Appraisals
Part 8 Players-Roles & Responsibilities
Part 9 Summary
We hope that you will benefit from this tutorial.
Author: Subject Coach
Added on: 16th Feb 2015
You must be logged in as Student to ask a Question.
None just yet!