Introduction to database management systems
Chapters
Data Models
A model is an abstraction process which hide superfluous details. Data modeling is
Used for representing entities and their relationship in database. Data model is a collection of concepts which is used to describe structure of a database which provides necessary means to abstraction. The structure of a database means that holds the data.
Types of Data Models
- High Level- Conceptual Data Model
- Low Level – Physical Data Model
- Relational or Representational
- Object-Oriented Data Model
- Object-Relational Model
High Level-conceptual Data Model: User level data model is high level or conceptual model. It provides concepts which are close to way that many users perceive data.
Low level-Physical Data Model: It provides concepts that describe details of how data is stored in computer model. Low-level data model is only for Computer specialists not for end-user.
Representation Data Model: It is between High level & Low level data model which provides concepts that may be understood by end-user but that are not too far removed from way data is organized by within computer. The most common model are:
- Relational Data Model : The Relational Model uses a collection of tables and relationship among those tables. Tables have multiple columns and each column has a unique name. The main advantage of this model is its ability to represent data in a simplified format. The process of manipulating record is simplified with use of certain key attributes used to retrieve data.
image source: wikimedia
- Network Model: The data in network model are represented by collection of records and relationships among data are represented by links, which can be viewed as pointers. The records in the database are organized as collection of arbitrary groups. The main advantage of this model is its representation of relationships between entities is implemented using pointers which allows representation of arbitrary relationship.
image source: wikimedia
- Hierarchy Model: A hierarchical data model the data is organized into a tree-like structure. The structure allows repeating information using parent/child relationships: each parent can have many children, but each child only has one parent.
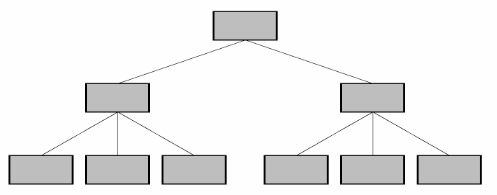
-
Object-Oriented Data Model: A data model is a logic organization of the real world objects (entities), constraints on them, and relationships among objects. A DB language is a concrete syntax for a data model. Example OBJECTSTORE or VERSANT
-
Object-Relational Model:
The object-oriented database product largely consists of classes, objects and inheritance that are supported in database schemas and in query language.
Description
This free tutorial covers the basics of database management system to help you with your understanding on the topic, Please note that this tutorial assumes that either you are a beginner or just want to brush up your understanding on DBMS
Tutorial covers the topics below
- What is DBMS?
- Architecture
- Data Models
- Data Schemas
- Data Independence
- Entity-Relation Model Basic Concept
- Entity-Relation Diagram Representation
- Generalization, Aggregation
- Codd's 12 Rules
- Relational Data Model
- Relational Algebra
- Structured Query Language
- Normalization
- Database Joins
- Storage System
- Indexing
- Hashing
- Transaction
- Concurrency Control and Deadlock
- Data Backup and Recovery
Audience
Absolute beginners or students who wish to brush up their understanding on DBMSes
Author: Subject Coach
Added on: 16th Sep 2015
You must be logged in as Student to ask a Question.
None just yet!