Beginners guide to MySQL and MariaDB
Chapters
Inserting and Selecing Data
Inserting data into Table
using mysql binary:
SQL INSERT INTO command is used to insert data into MySQL table.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO table_name
( field1, field2,...fieldN )
VALUES
( value1, value2,...valueN );
For string data types we keep values into single or double quote while inserting.
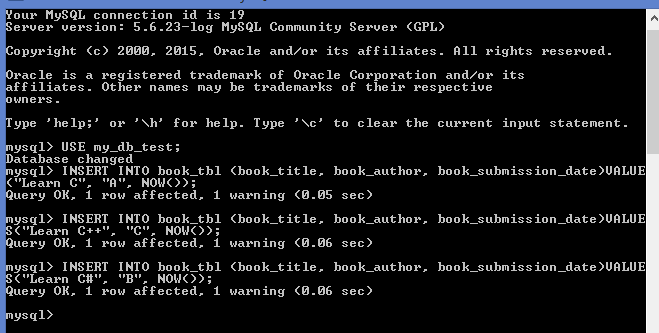
INSERT INTO book_tbl (
book_title,
book_author,
book_submission_date
) VALUES ("Learn C", "A", NOW()) ;
INSERT INTO book_tbl (
book_title,
book_author,
book_submission_date
)
VALUES
("Learn C++", "C", NOW()) ;
INSERT INTO book_tbl (
book_title,
book_author,
book_submission_date
)
VALUES
("Learn C#", "B", NOW()) ;
To achieve same stuff from a PHP Script here is how its done
Insert into MySQL using PHP PDO
Inserting using PDO follows same principles as we have seem so far, an example is shown below
<?php
$server = "localhost";
$user = "username";
$pwd = "password";
try {
$connection = new PDO("mysql:host=$server;dbname=testDB", $user, $pwd);
// PDO can throw exceptions rather than Fatal errors, so let's change the error mode to exception
$connection->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "INSERT INTO book_tbl (
book_title,
book_author,
book_submission_date
) VALUES (?, ?, ?) ;";
$insert = $sql->prepare($sql);
$insert->execute(array("Learn C","A",time());
echo "A new record was inserted into book_tbl";
}
catch(PDOException $e)
{
echo "Connection failed: " . $e->getMessage();
}
?>
Selecting data
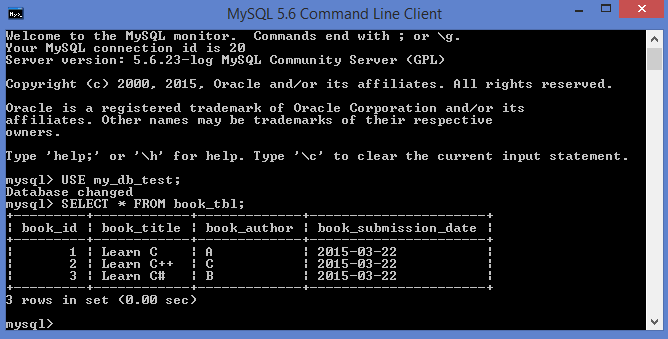
SELECT Table using mysql binary:
In MySQL SELECT command is used to fetch data from database.
Syntax:
SELECT field1, field2,...fieldN table_name1, table_name2...
[WHERE Clause]
[OFFSET M ][LIMIT N]
- one or more fields can be fetched in a single SELECT command.
- (*) in SELECT will return all fields.
- WHERE clause is used to specify any condition.
- LIMIT attribute is used to limit the number of return.
From a PHP script getting hold of your saved data is as simple as shown below
<?php
$server = "localhost";
$user = "username";
$pwd = "password";
try {
$connection = new PDO("mysql:host=$server;dbname=testDB", $user, $pwd);
$connection->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "select * from book_tbl;";
$select = $sql->prepare($sql);
$select->execute();
$result = $select->fetchAll();
var_dump($result);
}
catch(PDOException $e)
{
echo "Connection failed: " . $e->getMessage();
}
?>
In the next part of this tutorial we will check out where clause of a select query.
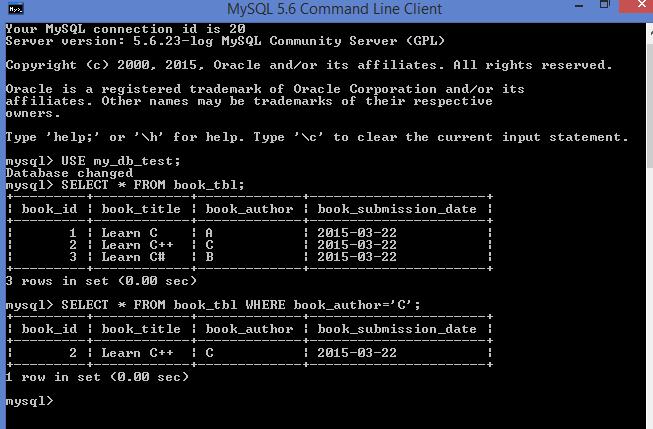
Where Clause
Syntax:
SELECT field1, field2,...fieldN table_name1, table_name2...
[WHERE condition1 [AND [OR]] condition2.....]]
AND or OR operators are used for specifying the condition.
|
Operator |
Description |
Example |
|
= |
Checks if values of two operands are equal or not, if yes then condition becomes true. |
(A = B) is not true. |
|
!= |
Checks if values of two operands are equal or not, if values are not equal then condition becomes true. |
(A != B) is true. |
|
> |
Checks if value of left operand is greater than the value of right operand, if yes then condition becomes true. |
(A > B) is not true. |
|
< |
Checks if value of left operand is less than the value of right operand, if yes then condition becomes true. |
(A < B) is true. |
|
>= |
Checks if value of left operand is greater than or equal to the value of right operand, if yes then condition becomes true. |
(A >= B) is not true. |
|
<= |
Checks if value of left operand is less than or equal to the value of right operand, if yes then condition becomes true. |
(A <= B) is true. |
|
= |
Checks if values of two operands are equal or not, if yes then condition becomes true. |
(A = B) is not true. |
Here is an example of using WHERE clause in your select statement.
If we have to rewrite our SELECT query to only show Books from book_tbl WHERE author is C. Here is how we do it from a PHP script with PDO extension
<?php
$server = "localhost";
$user = "username";
$pwd = "password";
try {
$connection = new PDO("mysql:host=$server;dbname=testDB", $user, $pwd);
$connection->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "select * from book_tbl where author='C';";
// above will only select books for author C
$select = $sql->prepare($sql);
$select->execute();
$result = $select->fetchAll();
var_dump($result);
}
catch(PDOException $e)
{
echo "Connection failed: " . $e->getMessage();
}
?>
Description
In this tutorial, we will cover few topics that will give you a heads on start to build your knowledge on. Topics that we will cover briefly but still providing enough information are listed below
- Overview
- Installing on Linux and Windows
- Some useful admin queries for starters
- Connection
- Create Database
- Drop Database
- Select Database
- Data Type
- Create Table
- Drop Table
- Inserting and Selecting data
- Where Clause
- Updating and deleting data
- Like Clause
- Sorting Result
- Using Joins
- Brief introduction to Regex, Transactions and Indexes
- Alter Command
- Temporary Tables
- Database Info
- Using Sequence
- Database Export and Import
- Resetting MySQL/MariaDB Administrator password
Audience
Absolute beginners looking to get a sneak peak into what MySQL. Please remember that this is not a full on guide but a quick introduction to the subject.
Learning Objectives
Get to know MySQL and MariaDB
Author: Subject Coach
Added on: 23rd Jun 2015
You must be logged in as Student to ask a Question.
None just yet!