Year 10+ Coordinate Geometry
Chapters
Using the Equation to Find the Intercepts
Using the Equation to Find the Intercepts
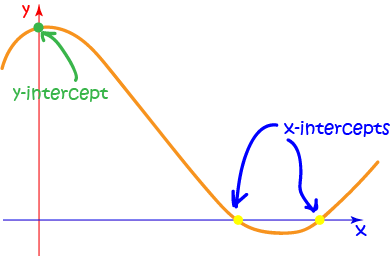
What are Intercepts?
Intercepts are places where the graph of a function cuts the axes. As there are two axes in the \(xy\)-plane, there are two different types of intercepts:
- \(x\)-intercepts occur when the graph crosses the \(x\)-axis.
- \(y\)-intercepts occur when the graph crosses the \(y\)-axis.
Finding the Intercepts
The \(x\)-intercepts lie on the \(x\)-axis, so their coordinates have the form \((x,0)\).
The \(y\)-intercepts lie on the \(y\)-axis, so their coordinates have the form \((0,y)\).
Examples
Example 1
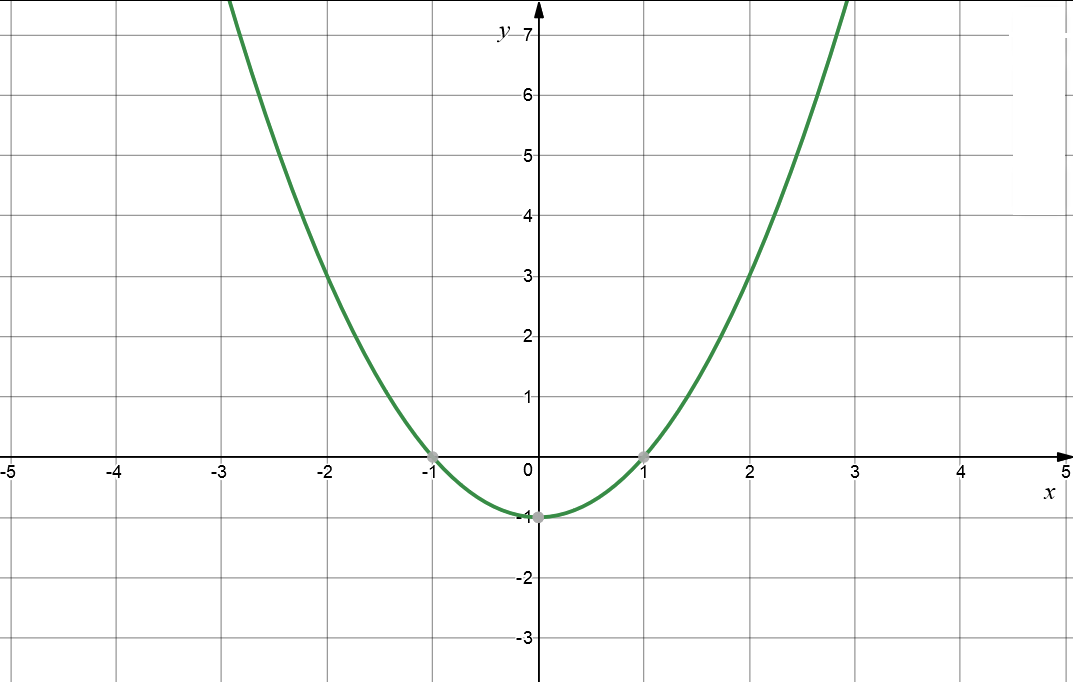
Find the intercepts of the function \(y= x^2 - 1\).
Solution:
The \(x\)-intercepts occur when y = 0:
The \(y\)-intercepts occur when x = 0:
The graph looks like:
Example 2
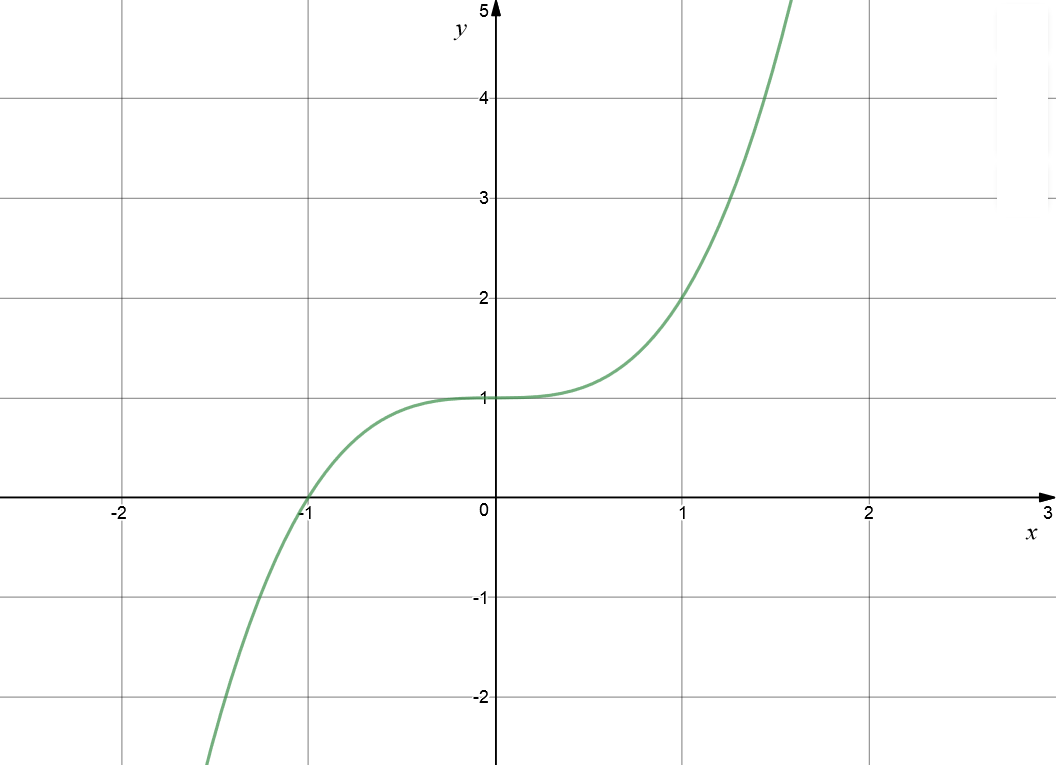
Find the intercepts of the function \(y= x^3 + 1\).
Solution:
The \(x\)-intercepts occur when y = 0:
The \(y\)-intercept occurs when x = 0:
The graph looks like:
Example 3
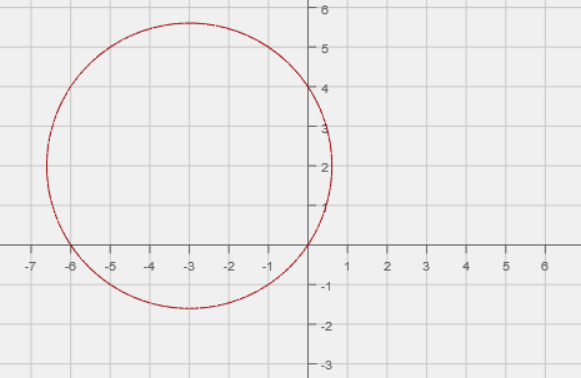
Find the intercepts of the function \( x^2 + 6x + y^2 - 4y = 0 \).
Solution:
The \(x\)-intercepts occur when y = 0:
The \(y\)-intercepts occur when x = 0:
The graph looks like:
Description
A coordinate geometry is a branch of geometry where the position of the points on the plane is defined with the help of an ordered pair of numbers also known as coordinates. In this tutorial series, you will learn about vast range of topics such as Cartesian Coordinates, Midpoint of a Line Segment etc
Audience
year 10 or higher, several chapters suitable for Year 8+ students.
Learning Objectives
Explore topics related to Coordinates Geometry
Author: Subject Coach
Added on: 27th Sep 2018
You must be logged in as Student to ask a Question.
None just yet!