To the point guide to PL/SQL
Chapters
Working with Conditional statements in PLSQL
PL/SQL Condition Statements are used to execute some instruction at specific condition.
Types of Condition Statements are:
- IF THEN Statement
- IF THEN ELSE Statement
- IF THEN ELSIF Statement
- Nested IF THEN ELSE Statement
IF statement verifies the condition and if the condition evaluates to TRUE, control is go to the first executable statement of the IF. If the condition evaluates to FALSE, control is go to the first executable statement after the END IF.
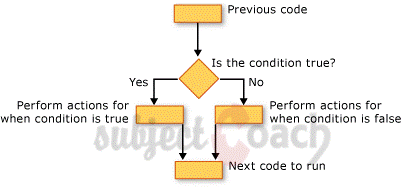
IF THEN Statement
The statement IF has a set of statements enclosed by the keywords THEN and END IF:
Syntax:
IF ( condition ) THEN
statement
END IF;
Example:
DECLARE
num INTEGER(2) := 8;
BEGIN
IF ( num <10 ) THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Condition is true: num is lesser');
END IF;
END;
/
Result:
Condition is true: num is lesser
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
IF THEN ELSE Statement
Syntax:
IF ( condition ) THEN
statement;
ELSE
statement;
END IF;
Example
DECLARE
num INTEGER(2) := 8;
BEGIN
IF ( num < 10 ) THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(num || ' is lesser');
ELSE
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(num || ' is not lesser');
END IF;
END;
/
Result
8 is lesser
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
IF THEN ELSIF Statement
Syntax
IF ( condition-1 ) THEN statement; ELSIF ( condition-2 ) THEN statement; ELSIF ( condition-3 ) THEN statement; ELSE statement; END IF;
Example
DECLARE
result CHAR(1) := 'A';
BEGIN
IF ( result = 'B' ) THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('B Grade');
ELSIF ( result = 'A' ) THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('A Grade');
ELSIF ( result = 'C' ) THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('C Grade');
ELSE
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Not Satisfactory');
END IF;
END;
/
Result
A Grade
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
Nested IF THEN ELSE Statement
Nested IF THEN ELSE Statement is logically same as IF THEN ELSIF. Let's familiarize ourselves with this statement' syntax and wrap it up with an example
Syntax
IF ( condition-1 ) THEN
statement;
ELSE
IF ( condition-2 ) THEN
statement;
ELSE
IF ( condition-3 ) THEN
statements;
END IF;
END IF;
END IF;
Example
DECLARE
colleagename CHAR(20) := 'IIN';
grade CHAR(1) := 'B';
BEGIN
IF ( gender = 'IIN' ) THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('IIN College!!!');
ELSE
IF ( grade = 'A' ) THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Grade A');
ELSIF ( result = 'B' ) THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Grade B');
ELSIF ( result = 'C' ) THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Grade C');
ELSIF ( result = 'D' ) THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Grade D');
ELSE
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Not Satisfactory');
END IF;
END IF;
END;
/
Result
Grade B PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
CASE Statement
It is used to evaluate the list of values; the CASE statement selects one of the statements to execute. The working of case is as shown below:
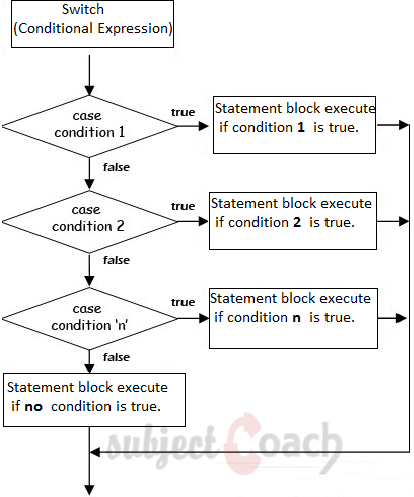
Syntax
CASE selector WHEN value1 THEN statement1; WHEN value2 THEN statement2; ELSE statement3; END CASE
Example
DECLARE
serial number := 5;
BEGIN
CASE serial
WHEN 1 THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('serial value 1');
WHEN 2 THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('serial value 2');
WHEN 3 THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('serial value 3');
ELSE
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('CASE not found'); END CASE;
END;
/
Result
CASE not found
PL/SQL procedure successfully operation.
Searched CASE Statement
PL/SQL searched CASE statement has not selector and attempt to match one or more WHEN clauses condition.
Syntax
CASE WHEN condition-1 THEN statement-1; WHEN condition-2 THEN statement-2; ELSE statement-3; END CASE;
Example
DECLARE
serial number := 3;
BEGIN
CASE
WHEN 1 THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('serial value 1');
WHEN 2 THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('serial value 2');
WHEN 3 THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('serial value 3'); ELSE
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('CASE not found'); END CASE;
END;
/
Result
serial value 3
PL/SQL procedure successfully operation.
Alright! so, we have learned some conditional statements with some really basic examples. In the next part of this guide we will explore Loop statements.
Description
This tutorial focus on PL/SQL and covers the below topics
- What is PL/SQL?
- Environment Setup
- Variables
- Data Types
- Constants
- Operators
- Conditions
- Loops
- Strings
- Arrays
- Procedures
- Functions
- Cursors
- Records
- Exceptions
- Packages
- Triggers
- Collections
- Transactions
- Date & Time
- Object Oriented
- DBMS Output
If you found any error with any of the docs please let us know.
Learning Objectives
Learn PL/SQL from a beginners perspective, this guide can also help you if you are trying to brush up your PLSQL skills
Author: Subject Coach
Added on: 20th Apr 2015
You must be logged in as Student to ask a Question.
None just yet!