Math Definitions - Letter D
Chapters
Duodecimal
Definition of Duodecimal
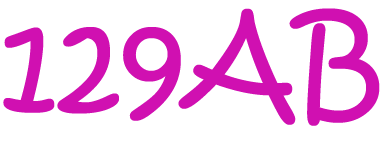
Duodecimal numbers are built out of the \(12\) digits, \(0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A\) and \(B\), although some people use other symbols such as an upside down \(1\) for \(A\) and an upside down \(2\) for \(B\).
The duodecimal system is a Base-12 number system.
Another name for the duodecimal number system is the dozenal number system.
The following are some examples of duodecimal numbers:
- The duodecimal number \(A\) is equal to the decimal number \(10\)
- The duodecimal number \(B\) is equal to the decimal number \(11\)
- The duodecimal number \(10\) is equal to the decimal number \(12\)
- The duodecimal number \(100\) is equal to the decimal number \(144\)
- The duodecimal number \(110\) is equal to the decimal number \(156\)
- The duodecimal number \(111\) is equal to the decimal number \(157\)
- The duodecimal number \(129AB\) is equal to the decimal number \(1 \times 12^4 + 2 \times 12^3 + 9 \times 12^2 + 10 \times 12 + 11 = 25,619\).
Description
The aim of this dictionary is to provide definitions to common mathematical terms. Students learn a new math skill every week at school, sometimes just before they start a new skill, if they want to look at what a specific term means, this is where this dictionary will become handy and a go-to guide for a studen
Audience
Year 1 to Year 12 students
Learning Objectives
Learn common math terms starting with letter D
Author: Subject Coach
Added on: 6th Feb 2018
You must be logged in as Student to ask a Question.
None just yet!